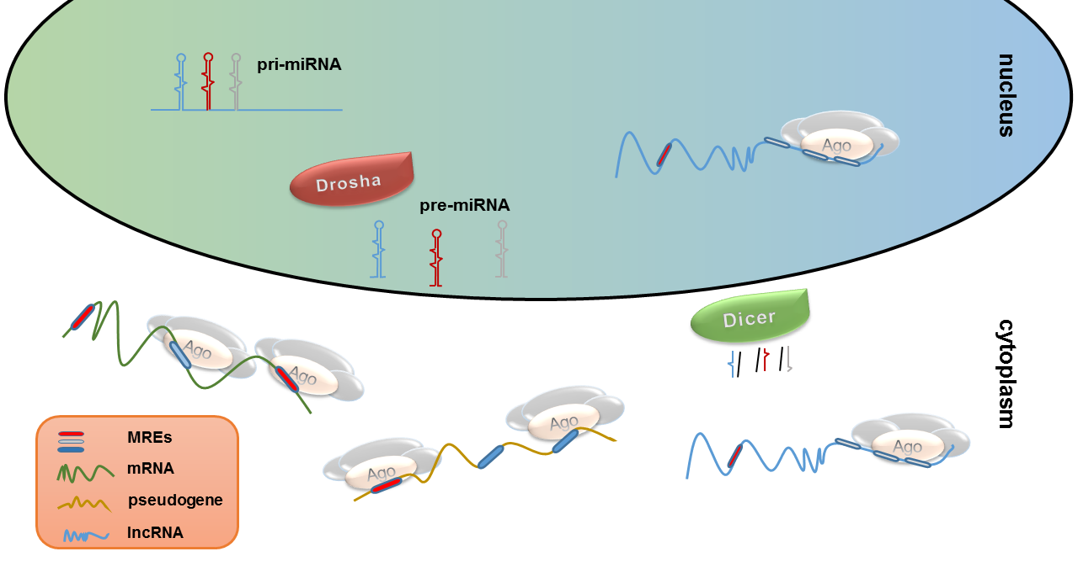
MicroRNA research has transformed our understanding of gene regulation, shedding light on the intricate roles these small RNA molecules play in biological processes. Pioneering the field, Nobel laureate Gary Ruvkun and his colleague Victor Ambros uncovered microRNAs while studying the C. elegans roundworm, leading to groundbreaking insights into how genes are controlled. Their work, which drew significant NIH funding, has paved the way for innovative therapies targeting diseases like heart conditions and cancer. Recognized by the scientific community, Ruvkun’s discovery is now celebrated as a crucial milestone that earned them the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. As the foundation for new medical advancements, microRNA research continues to captivate researchers and hold immense promise for future therapeutic applications.
The exploration of small non-coding RNAs, such as microRNAs, represents a revolutionary advancement in the realm of gene control mechanisms. Initial investigations by scientists in 1992, notably Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros, unveiled the significance of these RNAs in regulating gene expression within cellular systems, specifically using the model organism C. elegans. Despite early skepticism, their findings have garnered increasing interest, fueled by substantial NIH funding that has supported ongoing research efforts. As foundational elements in clinical applications, the implications of these tiny RNA molecules have been increasingly recognized, culminating in the prestigious 2024 Nobel Prize attribution. With strong potential for treating various diseases, the field of small RNA research is evolving rapidly, promising to reshape our understanding of genetics and medicine.
The Revolutionary Role of microRNA in Gene Regulation
MicroRNA research has brought forth a transformative understanding of gene regulation, particularly as illustrated by the groundbreaking work of Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros in the 1990s. Their discovery of microRNAs in the model organism C. elegans unveiled a complex layer of genetic control that was previously overlooked. By regulating gene expression at the post-transcriptional level, microRNAs influence various biological processes, including development and cellular function. As research progressed, it became evident that these tiny RNA molecules were not only vital in worms but also held significant implications for higher organisms, including humans.
The relevance of microRNAs has escalated dramatically over the past few decades, transitioning from a niche field of study to a cornerstone in molecular biology. The ongoing exploration of microRNAs has shifted the focus towards their therapeutic potential, with clinical trials targeting diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders proving their importance in medical science. This broadening interest underscores a vital realization within the scientific community: microRNA plays a critical role across species, bridging cellular functions from simple organisms to complex human systems.
Gary Ruvkun: A Pioneer in RNA Research
Gary Ruvkun’s pioneering contributions to RNA research have not only earned him the prestigious Nobel Prize in 2024 but have solidified his status as a cornerstone in the field of genetics. Initially, his groundbreaking work on microRNA was met with skepticism, as the scientific community struggled to recognize its implications for gene regulation. However, Ruvkun, alongside his collaborator Victor Ambros, persevered, and their findings have led to significant advancements in our understanding of genetic expression and its underlying mechanisms. Their commitment to uncovering the roles of microRNAs has reshaped molecular biology, paving the way for new therapeutic approaches.
Ruvkun’s journey from initial discovery to Nobel recognition illustrates the importance of sustained research, much of which has been funded through NIH grants. This federal support has been essential in advancing scientific inquiries that fuel innovation and discovery. By maintaining a focus on basic scientific research rather than immediate commercial applications, Ruvkun emphasizes the long-term benefits that arise from exploring fundamental biological questions. His work exemplifies how government investment in science not only cultivates knowledge but also stimulates economic growth and technological advancement.
NIH Funding: Fueling Scientific Breakthroughs
Over the past four decades, NIH funding has played a pivotal role in supporting Gary Ruvkun’s research and the wider field of microRNA studies. The federal investment, amounting to approximately $150,000 per year, has facilitated the exploration of gene regulation mechanisms and their implications for human health. Ruvkun’s lab, which operates with a smaller team, exemplifies how strategic funding can lead to significant advancements without the need for overwhelming resources. This approach allows for the nurturing of highly educated scientists, contributing to a vibrant research community that seeks to uncover the intricacies of molecular biology.
The strategic importance of NIH funding cannot be overstated, as it reflects a broader commitment to fostering scientific innovation that underpins the U.S. economy. Ruvkun points out that many top companies today have emerged from research initially supported by federal grants, illustrating a direct correlation between governmental investment and the growth of biotechnology sectors. With concerns over potential cuts to federal funding, scientists like Ruvkun stress the need for sustained investment to ensure the continuation of groundbreaking research that not only impacts science but also enhances the nation’s standing as a global leader in technology and healthcare.
C. elegans: The Model Organism for Genetic Research
The choice of C. elegans as a model organism has had a profound impact on genetic research, particularly in understanding the role of microRNAs in gene regulation. This nematode, with its simple anatomy and transparent body, allows scientists to observe genetic processes in real-time, providing valuable insights into cellular mechanisms. Gary Ruvkun and his collaborators leveraged the strengths of C. elegans to uncover the role of microRNAs – a discovery that has since spurred a wealth of research across various biological fields. The simplicity of this organism belies its critical contributions to advancing our understanding of more complex systems, including human health.
The versatility of C. elegans transcends its limitations, as this model organism continues to contribute to diverse areas of biology. Researchers have built upon Ruvkun’s foundational work, exploring how microRNAs govern development, cellular differentiation, and responses to environmental changes in various species. The findings derived from C. elegans research highlight the evolutionary conservation of gene regulation mechanisms, which has opened avenues for exploring genetic diseases in humans. As studies in C. elegans expand, the insights gained underline its enduring significance in the field of genetics.
The Intersection of Basic Research and Pharmaceutical Innovation
Gary Ruvkun’s discoveries have played an integral role in bridging the gap between basic research and pharmaceutical innovation. His work on microRNAs has laid the groundwork for therapies targeting multiple diseases, underscoring the interplay between academic research and clinical application. Major pharmaceutical companies, such as Alnylam, have emerged from this rich field of study, focusing on RNA interference therapeutics that stem from fundamental discoveries. The evolution of these breakthroughs illustrates the potential of basic research to stimulate development pathways, even as it nurtures an environment conducive to scientific inquiry.
The transition from groundbreaking discoveries in the lab to real-world treatments is often a lengthy process, yet Ruvkun’s experience demonstrates the substantial impact that foundational research can have on public health. By focusing on the underlying mechanisms of diseases, scientists develop targeted therapies that improve patient outcomes. This synergy between academia and industry showcases the vital role government funding plays in fostering innovation, potentially saving millions of lives. Ruvkun’s pride in witnessing the growth of biotechnology companies from basic research reflects a successful model wherein scientific inquiry leads to tangible benefits for society.
The Promise of RNA Therapies for Future Healthcare
As research continues to evolve, the potential of RNA therapies, particularly those based on microRNA mechanisms, holds great promise for the future of healthcare. Clinical trials investigating the therapeutic applications of microRNAs for diseases like cancer, heart disease, and neurodegenerative disorders underscore a shift towards precision medicine. These innovations are built upon decades of fundamental research pioneered by scientists like Gary Ruvkun, highlighting the profound impact of basic scientific inquiry on modern medicine. The ongoing exploration of RNA biology not only enhances treatment options but also informs our understanding of disease mechanisms at a molecular level.
The pursuit of RNA-based therapies reflects broader trends in personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to individual genetic profiles. As more therapeutic modalities enter clinical practice, we can anticipate a new era of healthcare that harnesses the power of microRNAs to address previously intractable diseases. The concerted efforts among researchers, supported by consistent funding from institutions like the NIH, will be crucial in realizing the full potential of these groundbreaking therapies. The discussions surrounding the future of RNA research and its applications will continue to inspire both scientific inquiry and clinical practice.
Navigating the Challenges of Research Funding
The landscape of scientific funding is an ongoing challenge for researchers like Gary Ruvkun, who have relied on federal support for their investigations into gene regulation and microRNA function. As discussions surrounding budget cuts to NIH funding circulate, the potential impact on research activities raises important questions about the future of scientific inquiry. Ruvkun’s experience reflects a growing concern among scientists: reduced funding could stifle innovation and drive promising talent away from research careers. The necessity for stable investment in science has become increasingly urgent to maintain the momentum of breakthrough discoveries.
Maintaining a balancing act between securing funding and conducting impactful research is a critical aspect of a scientist’s career. Ruvkun underlines the importance of emphasizing the value of scientific investigations that may not lead to immediate profit but lay the groundwork for future advancements. Reinforcing the need for continued financial support for basic research is crucial, as it directly influences the trajectory of emerging fields like microRNA studies. Ensuring that government funding remains stable is a priority for nurturing the next generation of science leaders, allowing them to thrive in an environment where fundamental research can flourish.
Establishing a Global Perspective on Genetic Research
As the realm of genetic research continues to expand, establishing a global perspective becomes essential for fostering international collaboration and sharing knowledge. Gary Ruvkun’s contributions to the understanding of microRNAs serve as a foundation upon which scientists around the world can build, exploring the implications of genetic regulation across diverse species. Collaborations between laboratories that focus on RNA biology can expedite the progress of therapies targeting genetic diseases, highlighting the importance of unity in scientific endeavors. By sharing findings and expertise, researchers can elevate the field of genetics, impacting healthcare globally.
The importance of a global approach in scientific research cannot be understated, particularly in areas such as RNA therapeutics that promise to revolutionize medicine. International funding schemes and partnerships can facilitate the exchange of innovative ideas and best practices, allowing scientists to work together effectively. As more researchers engage with the data produced by studies like Ruvkun’s, they can contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of genetic mechanisms that govern health and disease. The collective knowledge gained through global collaboration has the potential to yield transformative changes in how we approach healthcare and disease management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is microRNA research and why is it significant?
MicroRNA research involves the study of small RNA molecules that play a critical role in gene regulation. This field is significant as it has transformed our understanding of how genes are controlled, leading to breakthroughs in various diseases, and it has applications in developing therapies for conditions such as cancer and heart disease.
How did Gary Ruvkun contribute to the field of microRNA research?
Gary Ruvkun, along with Victor Ambros, discovered microRNAs in the early 1990s while studying the C. elegans roundworm. Their findings revealed a new level of gene regulation, laying the groundwork for extensive research into microRNAs’ roles in various biological processes and diseases.
What impact did the NIH have on microRNA research?
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) provided critical funding that supported decades of microRNA research, enabling scientists like Gary Ruvkun to explore gene regulation mechanisms and facilitating the advancement of therapies targeting diseases like Cancer and Alzheimer’s.
Why did Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros not receive immediate recognition for their discovery of microRNAs?
Initially, microRNA research did not attract widespread interest, as it was uncertain whether the genes studied in C. elegans had a significant impact on other species, including humans. Recognition grew over time as the importance of microRNAs in gene regulation became clearer.
What potential therapies are emerging from microRNA research?
MicroRNA research has led to the development of promising therapies for several diseases, including cancer, Crohn’s disease, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s. These therapies are currently undergoing clinical trials and aim to leverage microRNAs for effective treatment options.
How has the understanding of microRNAs changed since their discovery?
Since their discovery, research has shown that microRNAs are fundamental in regulating gene expression across various organisms, not just C. elegans. Today, it is understood that they play critical roles in developmental processes and the functioning of organisms.
What is the future of microRNA research in relation to the Nobel Prize?
The 2024 Nobel Prize awarded to Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros highlights the significance of microRNA research, which is expected to continue evolving with increased funding and interest, leading to novel insights and therapeutic applications in genetics and medicine.
How do microRNAs regulate gene expression?
MicroRNAs regulate gene expression by binding to messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules, leading to either the degradation of the mRNA or the inhibition of protein translation. This process is essential for controlling various cellular functions and pathways.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Nobel Prize Achievement | Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros discovered microRNA in 1992, earning the Nobel Prize in 2024. |
| Initial Reception | Their early work was met with skepticism and lacked wide recognition within the evolutionary biology community. |
| Research Funding | The research was primarily funded by NIH grants, which played a crucial role in advancing their studies. |
| Impact on Medicine | MicroRNA therapies are now in clinical trials for treating heart disease, cancer, and other diseases. |
| Global Interest | The field of microRNA research has rapidly grown, attracting attention from various scientific disciplines. |
| Fundamental Findings | MicroRNAs are essential for gene regulation and the development of organisms. |
| Federal Support | Federal funding has been vital for supporting lab research and scientific advancements. |
| Advancements in Biotechnology | Breakthroughs in microRNA research have led to the emergence of biotech companies focused on RNA therapeutics. |
Summary
MicroRNA research has transformed our understanding of gene regulation and has significant implications for medicine. The groundbreaking work of Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros paved the way for new therapeutic strategies in treating various diseases. As microRNA continues to reveal its potential in clinical settings and research advancements flourish, the future of this field remains bright, promising innovative solutions for complex health challenges.